The Ultimate Guide to BaoXing Bags
Explore the latest trends and styles in BaoXing bags.
Charge Without Chains: The Future of Wireless Power
Discover the groundbreaking future of wireless power! Say goodbye to charging chaos and embrace freedom with cutting-edge technology.
How Wireless Power Works: The Science Behind Free Charging
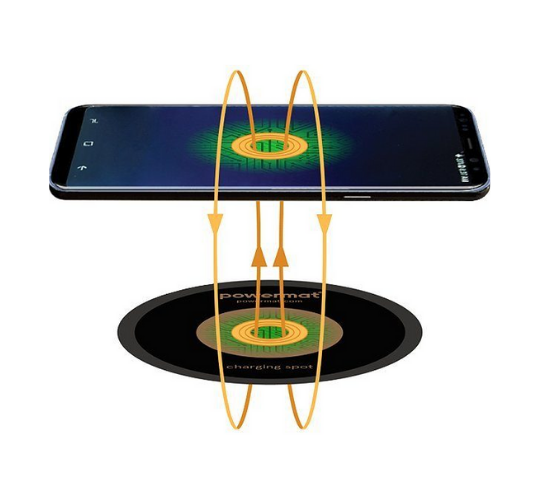
Wireless power technology, also known as wireless charging, utilizes electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between two objects. This process primarily involves two key components: a transmitter, which is connected to a power source, and a receiver, typically found in devices like smartphones or electric toothbrushes. When the transmitter sends out electromagnetic waves, the receiver converts these waves back into electricity, allowing the device to charge without the need for physical connections. The most widely used method for this technology is inductive charging, which relies on coils of wire in both the transmitter and receiver to create a magnetic field.
At the heart of how wireless power works is the principle of electromagnetic induction. Essentially, when alternating current flows through the transmitter's coil, it generates a magnetic field. When a compatible receiver coil is placed within this field, an electric current is induced in the receiver coil, thus charging the device. This seamless charging experience not only simplifies the process for users but also protects devices from wear and tear often caused by traditional charging cables. As technology advances, we can expect even greater efficiency and broader applications of wireless power in our daily lives, making it a vital aspect of our evolving electric ecosystem.
Counter-Strike is a highly popular first-person shooter game that has been a staple in competitive gaming since its release. Players team up as either terrorists or counter-terrorists, engaging in tactical battles across various maps and game modes. For those who need to keep their devices charged while gaming, check out these Top 10 Nightstand Chargers for Apple Watch to ensure you stay powered up for your next match.
The Benefits of Going Wireless: Why the Future is Power Without Cords
In today's fast-paced world, the shift towards wireless technology has revolutionized the way we interact with our devices. The benefits of going wireless are manifold, promising not only greater convenience but also enhanced mobility. Without the hassle of tangled cords and charging cables, users can enjoy a cleaner, more organized space, whether in their homes or offices. Wireless devices, from headphones to charging stations, provide the freedom to move about without being tethered to a wall socket, making it easier to multitask and stay connected on the go.
Moreover, going wireless is not just about convenience; it also contributes to a more efficient and environmentally friendly lifestyle. By reducing the number of cords and cables, we lower electronic waste and promote sustainable technology practices. For instance, with the adoption of wireless charging, the energy consumption can be optimized, as devices can charge only when they need it. As technology advances, the future looks bright for wireless solutions, paving the way for smarter homes and offices powered without the constraints of traditional wiring.
What are the Challenges Facing Wireless Power Technology Today?
The advent of wireless power technology has opened new frontiers in various industries, yet it faces several significant challenges today. One of the primary obstacles is efficiency, as current wireless charging systems typically demonstrate lower energy transfer rates compared to traditional wired connections. This inefficiency not only affects charge times but also limits the practicality of wireless solutions in larger applications. Additionally, compatibility remains a concern, as different devices often require specific charging standards, making it challenging to establish a universal wireless charging solution.
Another major hurdle for wireless power technology is regulatory compliance. As governments and organizations strive to promote safety and standardization, the technology must adapt to numerous regulations regarding electromagnetic fields. Furthermore, concerns regarding health effects stemming from prolonged exposure to these electromagnetic fields also need to be addressed. Lastly, consumer adoption can be hindered by a perception that wireless power systems are expensive or less reliable than their wired counterparts, ultimately impacting the growth of this innovative technology.